Open API specification, previously known as Swagger specification defines standard, language-agnostic interface to RESTful API’s which allows to understand service’s capabilities without access the code. Where you can keep your documentation attached with the evolution of your project. With Swagger UI you will have a web interface that allows you to easily interact with API’s resources without having any implamentation in place. An Open API specification can then be used by code generation tools to generate servers and clients, testing tools and many more. To know more about Swagger please visit it’s official web site here. NOTE: If you need to know what tools you need to have installed in yout computer in order to create a Spring Boot basic project, please refer my previous post: Spring Boot
Then execute this command in your terminal:
spring init --dependencies=web,lombok --language=java --build=gradle boot-configuration
This is the build.gradle generated file:
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.5'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.11.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
def springfoxVersion = '3.0.0'
def springfoxUiVersion = '2.9.2'
group = 'com.jos.dem.swagger'
version = '1.0.0-SNAPSHOT'
configurations {
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Then add swagger dependencies in your build.gradle file
dependencies {
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger2:${springfoxVersion}"
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger-ui:${springfoxUiVersion}"
}
Next step is to create a Swagger Configuration file:
package com.jos.dem.swagger.config;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.Set;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SwaggerConfig {
private final ApplicationProperties applicationProperties;
@Bean
public Docket createDocket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false)
.protocols(Set.of("https", "http"))
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage(applicationProperties.getBasePackage()))
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title(applicationProperties.getTitle())
.description(applicationProperties.getDescription())
.termsOfServiceUrl(applicationProperties.getTerms())
.version(applicationProperties.getVersion())
.build();
}
}
Swagger 2 is enabled through the @EnableSwagger2 annotation. With Docket bean definition we are able to provide methods for configuration, it has a select() method and returns an instance of ApiSelectorBuilder, which provides a way to control the endpoints exposed by Swagger. Predicates in RequestHandlers can be configured with the help of RequestHandlerSelectors and PathSelectors.
Controller Documentation
Now it is time to see the most common annotations in a RestController in order to create our API documentation.
package com.jos.dem.swagger.controller;
import com.jos.dem.swagger.command.UserCommand;
import com.jos.dem.swagger.model.User;
import com.jos.dem.swagger.service.UserService;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses;
import java.util.List;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Api(tags = "knows how receive manage user requests")
@Validated
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserController {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private final UserService userService;
@ApiOperation(value = "Getting all users")
@ApiResponses(
value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 200, message = "Getting all users"),
@ApiResponse(code = 400, message = "Bad request"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500, message = "Something went wrong")
})
@GetMapping
public List<User> getAll() {
log.info("Getting all users");
return userService.getAll();
}
@ApiOperation(value = "Get user by uuid")
@ApiResponses(
value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 200, message = "Getting all users"),
@ApiResponse(code = 400, message = "Bad request"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500, message = "Something went wrong")
})
@ApiImplicitParams(
value = {
@ApiImplicitParam(
name = "uuid",
required = true,
dataType = "string",
paramType = "path",
value = "User's uuid")
})
@GetMapping(value = "/{uuid}")
public User getByUuid(
@PathVariable
@Pattern(
regexp =
"^[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}$",
message = "Invalid uuid format")
String uuid) {
log.info("Getting user by uuid: " + uuid);
return userService.getByUuid(uuid);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "Create user")
@ApiResponses(
value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 200, message = "User created"),
@ApiResponse(code = 400, message = "Bad request"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500, message = "Something went wrong")
})
@PostMapping(consumes = "application/json")
public User create(@Valid @RequestBody UserCommand command) {
log.info("Saving user: w/uuid: " + command.getUuid());
return userService.create(command);
}
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleException(ConstraintViolationException ce) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(ce.getMessage(), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
Where:
@ApiDescribe logical grouping of operations by resource@ApiOperationDescribes an operation against a specific path.@ApiResponsesIs a list of responses provided by the API operation@ApiImplicitParamsRepresent parameters in an API operation. Please go here to see the complete list of attributes we can set in our params.
Here is our user domain transfer object:
package com.jos.dem.swagger.command;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@ApiModel(value = "UserModel", description = "Model who represents an user entity")
public class UserDto {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's uuid", required = true)
@Pattern(regexp = "^[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}$", message = "Invalid uuid format")
private String uuid;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's name", required = true)
@NotBlank(message = "name is required")
private String name;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's email", required = true)
@NotBlank(message = "email is required")
@Email
private String email;
}
Where:
@ApiModelProvides additional information about Swagger models. This translates to the Model Object in the Swagger Specification.@ApiModelPropertyAdds and manipulates data of a model property.
So, now if you execute our application:
gradle bootRun
You should be able to hit the endpoint to create request to your API using Swagger: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
Swagger Results
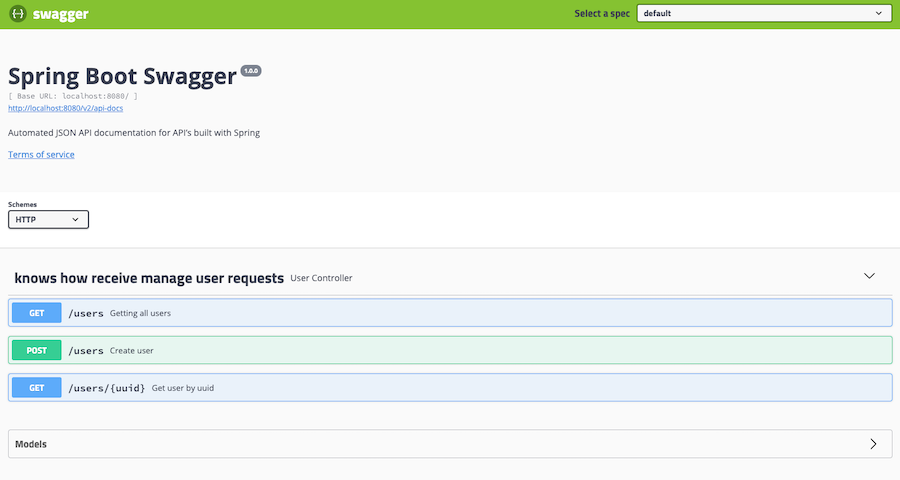
Using Maven
You can do the same using Maven, the only difference is that you need to specify --build=maven parameter in the spring init command line:
spring init --dependencies=web,lombok --language=java --build=maven boot-configuration
This is the pom.xml file generated:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.jos.dem.swagger</groupId>
<artifactId>boot-configuration</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>boot-configuration</name>
<description>com.jos.dem.swagger</description>
<properties>
<java.version>15</java.version>
<springfox-version>3.0.0</springfox-version>
<springfox-ui-version>2.9.2</springfox-ui-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>${springfox-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>${springfox-ui-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
To run the project with Maven:
mvn spring-boot:run
To browse the code go here, to download the project:
git clone git@github.com:josdem/swagger-spring.git
cd boot-configuration
