Swagger is a simple yet powerful representation of your RESTful API. With Swagger you can keep your documentation attached with the evolution of your code and with Swagger UI you’ll have a web interface that allows you to easily create GET and POST request to your API.
Java Configuration
First you need to add swagger dependencies in your build.gradle file
def springfoxVersion = '2.4.0'
dependencies {
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger2:${springfoxVersion}"
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger-ui:${springfoxVersion}"
}
The complete build.gradle looks like this:
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.bmuschko:gradle-tomcat-plugin:2.2.2'
}
}
ext{
springVersion = '4.3.1.RELEASE'
springfoxVersion = '2.4.0'
}
apply plugin: "groovy"
apply plugin: "application"
apply plugin: 'com.bmuschko.tomcat'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
def tomcatVersion = '8.0.27'
compile 'org.codehaus.groovy:groovy-all:2.1.3'
compile "org.springframework:spring-webmvc:$springVersion"
compile 'javax.servlet:javax.servlet-api:3.1.0'
compile 'com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:2.8.0'
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger2:${springfoxVersion}"
compile "io.springfox:springfox-swagger-ui:${springfoxVersion}"
tomcat "org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-core:${tomcatVersion}",
"org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-logging-juli:${tomcatVersion}",
"org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-jasper:${tomcatVersion}"
}
tomcat {
contextPath = '/'
}
Then you need to create a Swagger Configuration file:
package com.jos.dem.swagger.config
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2
@EnableSwagger2
class ApplicationSwaggerConfig{
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
}
Add ApplicationSwaggerConfiguration to your ApplicationInitializer
package com.jos.dem.swagger.initializer
import javax.servlet.ServletContext
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
import javax.servlet.ServletException
import com.jos.dem.swagger.config.AppConfig
import com.jos.dem.swagger.config.ApplicationSwaggerConfig
class ApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext()
ctx.register(AppConfig.class)
ctx.register(ApplicationSwaggerConfig.class)
ctx.setServletContext(servletContext)
Dynamic dynamic = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(ctx))
dynamic.addMapping("/")
dynamic.setLoadOnStartup(1)
}
}
Since is Java configuration, you don’t have the luxury of auto-configuration of your resource handlers. Swagger UI adds a set of resources which you must configure as part of a class that extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, and is annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
package com.jos.dem.swagger.config
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages ="com.jos.dem.swagger")
@EnableWebMvc
class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("swagger-ui.html")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
}
}
Controller Documentation
If you need to pass parameters to your controller using GET, you can document it as follow:
package com.jos.dem.swagger.controller
import static org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod.GET
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import io.swagger.annotations.Api
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams
import com.jos.dem.swagger.service.UserService
import com.jos.dem.swagger.command.UserCommand
import com.jos.dem.swagger.model.User
@Api(description="knows how receive manage user requests")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users/*")
class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService
@ApiImplicitParams([
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "uuid", value = "User's uuid", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "query")
])
@RequestMapping(method = GET, value = "/")
User getUserByUuid(UserCommand command){
userService.getByUuid(command.uuid)
}
}
@ApiImplicitParams Represents a single parameter in an API Operation, in this case user’s uuid. You can also document your model using @ApiModel
package com.jos.dem.swagger.command
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty
@ApiModel(value="UserCommand", description="Generic command from users")
class UserCommand {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's uuid", allowableValues = "aphanumeric")
String uuid
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's name", allowableValues = "text")
String name
@ApiModelProperty(value = "User's email", allowableValues = "email@domain")
String email
}
So when you do a POST Swagger uses the @ApiModelProperty to represent the data. Here is the controller with both methods.
dckage com.jos.dem.swagger.controller
import static org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod.GET
import static org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod.POST
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import io.swagger.annotations.Api
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams
import com.jos.dem.swagger.service.UserService
import com.jos.dem.swagger.command.UserCommand
import com.jos.dem.swagger.model.User
@Api(description="knows how receive manage user requests")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users/*")
class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService
@ApiImplicitParams([
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "uuid", value = "User's uuid", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "query")
])
@RequestMapping(method = GET, value = "/")
User getUserByUuid(UserCommand command){
userService.getByUuid(command.uuid)
}
@RequestMapping(method = POST, consumes="application/json")
User create(@RequestBody UserCommand command){
userService.create(command)
}
}
The endpoint to create request to your API using Swagger is: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
Swagger Results
View
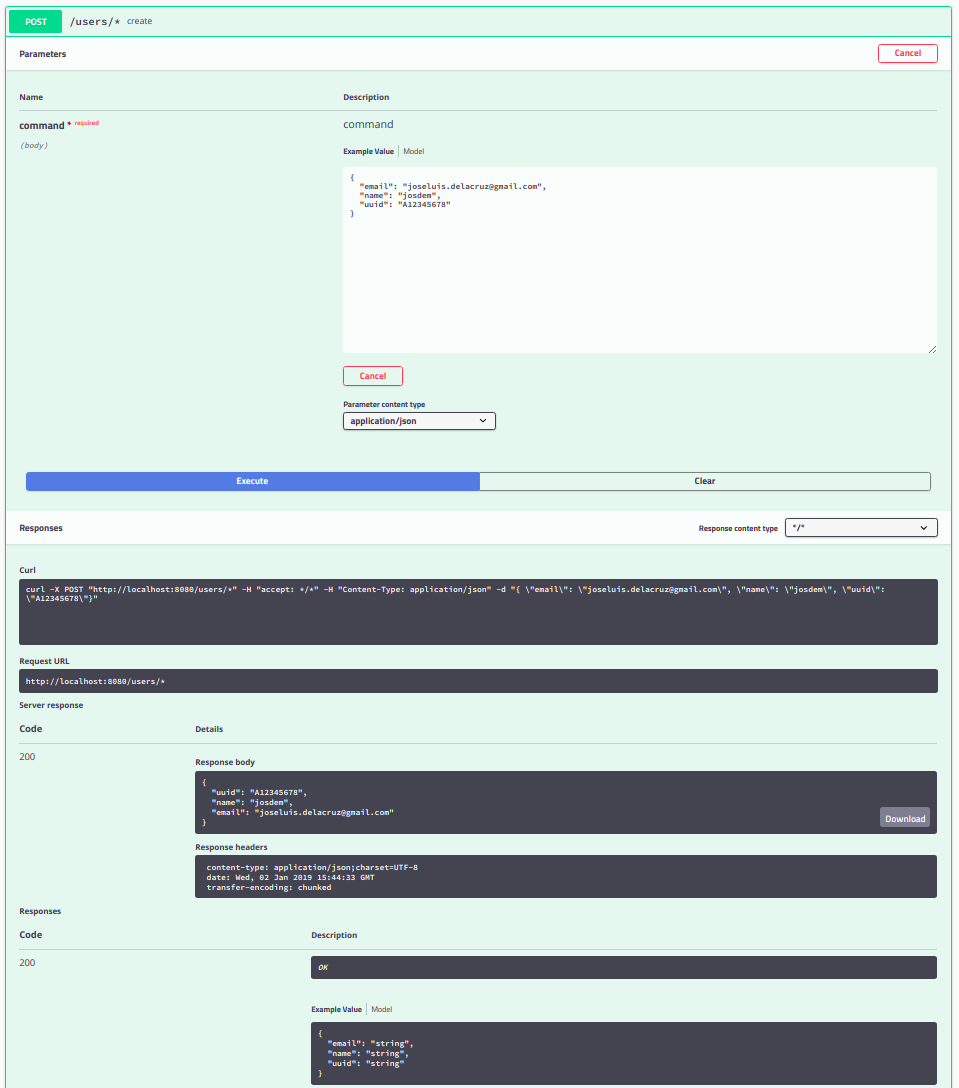
Post
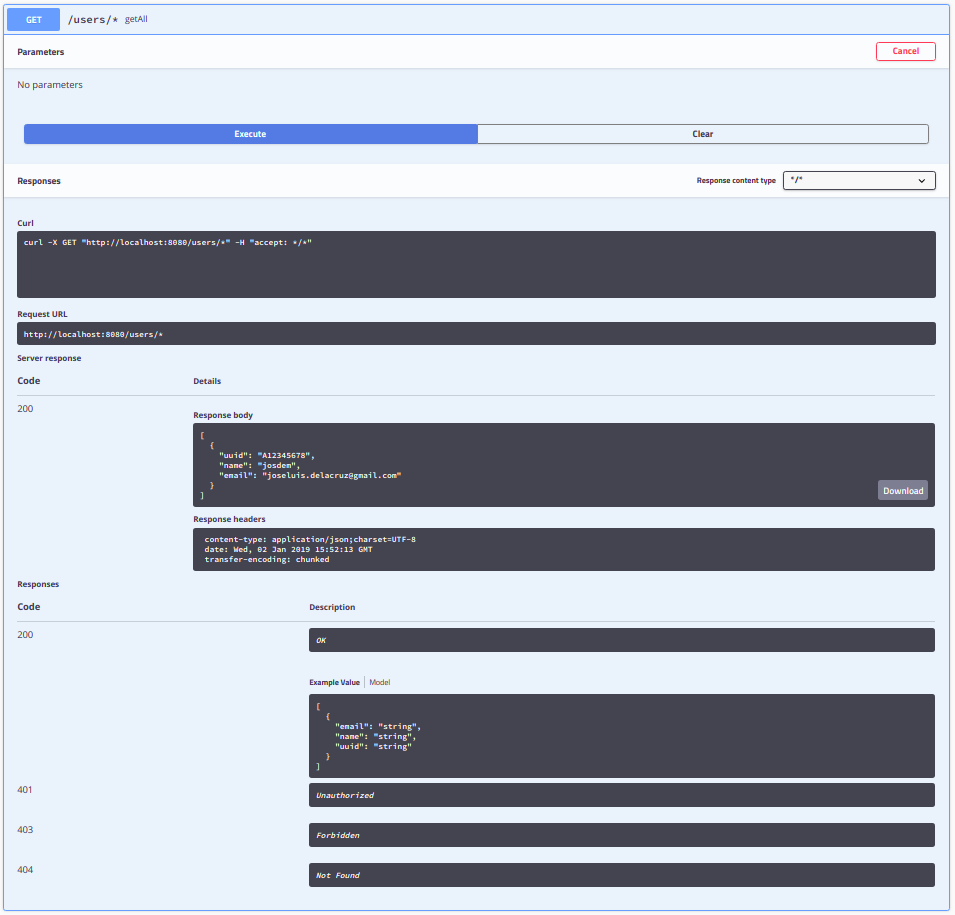
Get
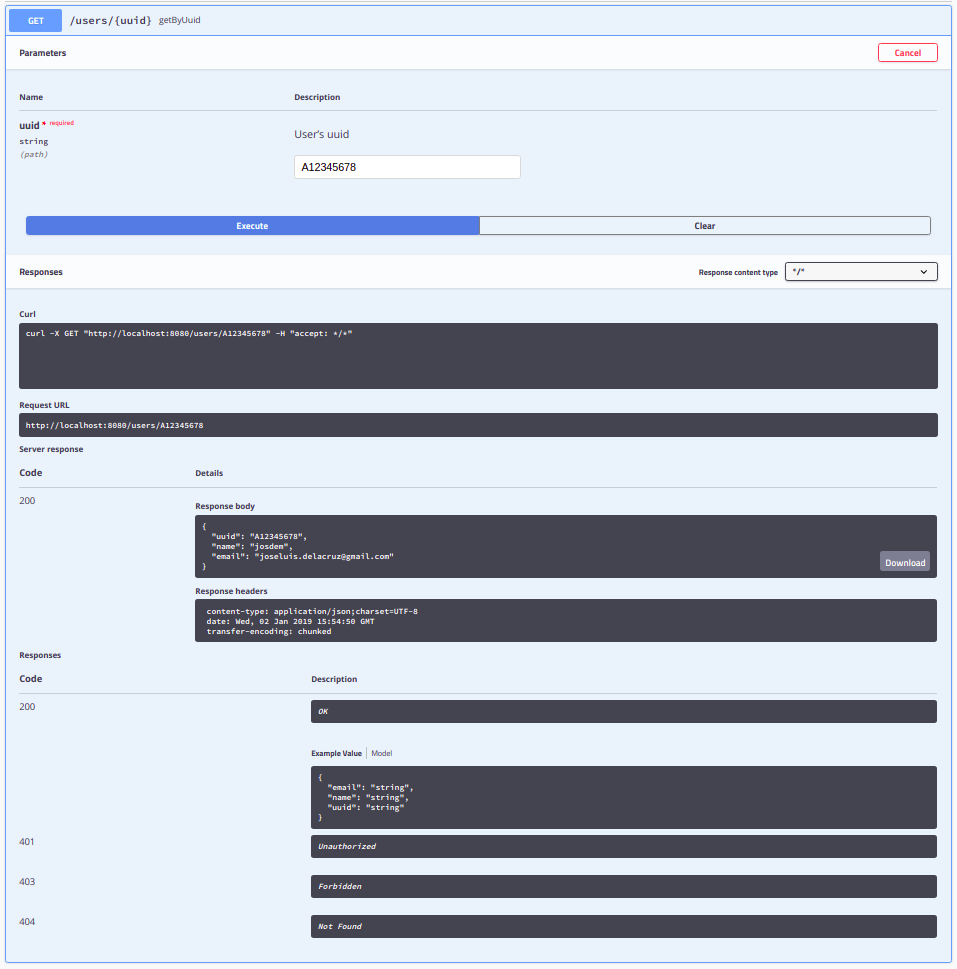
To download the project:
git clone https://github.com/josdem/swagger-spring.git
cd xml-configuration
To run the project.
gradle tomcatRun
